Renaissance Florence vs Silicon Valley: Entropy & Innovation
July 27th, 2025Why does the world’s most advanced innovation hub produce fewer breakthroughs per capita than a Renaissance city-state? The answer lies in entropy—the hidden force that determines whether innovation systems thrive or collapse.
Innovation systems operate within universal constraints established by Information Physics principles. Renaissance Florence and Silicon Valley face identical fundamental conditions, yet achieve dramatically different outcomes based on how effectively innovators navigate entropy gradients using time, information, and tools.
The mathematical analysis reveals a startling reality: Silicon Valley operates at entropy level , exceeding the critical threshold where systems cascade into dysfunction. Florence achieved , remaining safely below the percolation limit where innovation becomes thermodynamically sustainable.
This comparison demonstrates that superior technology cannot compensate for high entropy when conscious agents struggle to navigate information processing constraints effectively.
Mathematical Foundation
Innovation systems operate within the unified Information Physics framework, where conscious agents navigate entropy gradients using discrete spacetime constraints. The mathematical principles governing cosmic evolution also determine innovation capacity at human scales.
System Entropy Change for Innovation
The fundamental relationship governing innovation capacity within any bounded system follows the Entropic Mechanics equation:
Where:
- : System entropy change achievable by innovator [dimensionless]
- : Operation class from Conservation of Boundaries framework [dimensionless]
- : Intent vector (magnitude and direction in entropy space) [dimensionless]
- : Positional energy multiplier [dimensionless]
This equation captures how operation-intent alignment, modulated by positional constraints, determines an innovator’s capacity to influence system entropy direction. Higher η values create exponentially greater resistance to change.
Information-Energy Density in Innovation Systems
Innovation activity generates measurable energy density through Landauer’s principle, connecting information processing to thermodynamic costs:
Where:
- : Bit processing rate density [bits·m⁻³·s⁻¹]
- : Landauer energy cost per bit [J]
The bit processing rate connects to innovation intensity:
Where:
- : Innovation-reaction term [s⁻¹]
- : Voxel hop time from electromagnetic lattice [s]
- : Gradient-dependent processing function [dimensionless]
Innovation processing activity increases where information gradients are strongest, generating measurable thermodynamic costs that determine long-term sustainability.
Percolation Threshold and Critical Transitions
Innovation systems undergo phase transitions at the critical entropy threshold:
- Below 0.45: Problems remain manageable, innovation sustainable
- At 0.45: System enters critical state, instability emerges
- Above 0.45: Cascading failures compound faster than solutions
This threshold represents the point where problems compound exponentially, explaining observable symptoms in high-entropy innovation environments.
Direct Comparison: Florence 1480 vs Silicon Valley 2025
The numbers tell a shocking story. Despite every technological advantage, Silicon Valley produces dramatically fewer innovators per capita than Renaissance Florence. The quantitative analysis reveals how identical fundamental constraints create vastly different outcomes based on entropy levels.
| Metric | Renaissance Florence (1480) | Silicon Valley (2025) | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 70,000 | ~7.7 million (Bay Area) | 110x larger |
| Major Innovators | 25-30 | ~200-300 | 10x more total |
| Innovation Rate | 3.9 per 10k | 0.32 per 10k | 12x decline |
| Average Entropy | 0.30 | 0.54 | 80% increase |
| System Efficiency (SEC) | 1.538 | 1.299 | 16% decline |
| Daily Energy Cost | ~170 kcal | ~1,560 kcal | 9.2x increase |
| Survival Duration | 90+ days | ~55 days | 39% reduction |
| Critical Threshold Status | SAFE () | EXCEEDED () | Past cascade |
Silicon Valley produces twelve times fewer innovators per capita despite being 110 times larger—a systemic failure, not measurement error. This demonstrates how identical fundamental constraints produce dramatically different outcomes based on entropy navigation effectiveness using time, information, and tools.
Navigation Tools Breaking Down
What separates thriving innovation systems from struggling ones? The answer lies in how effectively innovators can use time and information to navigate entropy constraints. Silicon Valley’s navigation failure manifests most clearly in how it handles the two primary resources conscious agents need for breakthrough innovation.
Time Compression Effects
Time horizons determine innovation depth. Florence and Silicon Valley approach temporal resources in fundamentally different ways.
Florence approach: Decades-long patronage provided time for deep exploration, enabling innovators to develop sophisticated strategies for navigating complexity and uncertainty.
Silicon Valley approach: 18-month venture capital runways create time scarcity, forcing shortcuts that prevent optimal solution development.
This temporal constraint differential creates the foundation for all subsequent entropy accumulation patterns. When innovators lack time to think deeply, every other constraint becomes exponentially harder to navigate.
Information Overload Dynamics
Information quality determines learning efficiency. The contrast between Florence and Silicon Valley reveals how signal-to-noise ratios affect innovation capacity.
Florence approach: Master-apprentice relationships created high signal-to-noise ratios, enabling efficient knowledge transfer and skill development through direct mentorship.
Silicon Valley approach: Stack Overflow chaos creates information entropy, overwhelming innovators with noise that drowns out valuable signals within cognitive bandwidth limitations.
When both primary navigation tools fail simultaneously—time compressed by venture capital cycles, information drowned in noise—innovators lose strategic capability. They become reactive rather than proactive, trapped in tactical responses instead of breakthrough thinking.
This breakdown reduces innovation capacity to near-zero regardless of available technological tools, explaining why superior resources cannot compensate for navigation failure.
The Percolation Crisis: Silicon Valley at the Edge
Silicon Valley has crossed a mathematical point of no return. At entropy level , it has exceeded the critical threshold where innovation systems undergo phase transitions. The system now operates in cascade territory where problems compound faster than solutions emerge.
Thermodynamic Analysis of Critical Transition
The percolation threshold represents more than a mathematical boundary—it marks the point where systems experience irreversible cascade failures. The universal collision-diffusion equation that governs cosmic evolution also applies to innovation systems:
When innovation systems exceed , entropy-generating processes dominate structure-forming dynamics, creating observable symptoms of system breakdown.
Observable Cascade Symptoms
At , Silicon Valley exhibits characteristic signs of systems operating beyond the critical threshold.
Observable cascade symptoms:
- Talent exodus: Engineers fleeing to lower-entropy environments (Austin, Miami, remote work)
- Shortened horizons: Focus shifting from moonshots to quick exits
- Cultural decay: “Tech bro” culture replacing builder culture
- Innovation slowdown: More unicorns, fewer breakthroughs
- Inequality spiral: Success increasingly concentrated among fewer players
Each symptom reflects mathematical proximity to cascade threshold where stable innovation patterns break down. The system can no longer maintain the conditions necessary for sustained breakthrough creation.
Entropy Breakdown: Why Silicon Valley Struggles
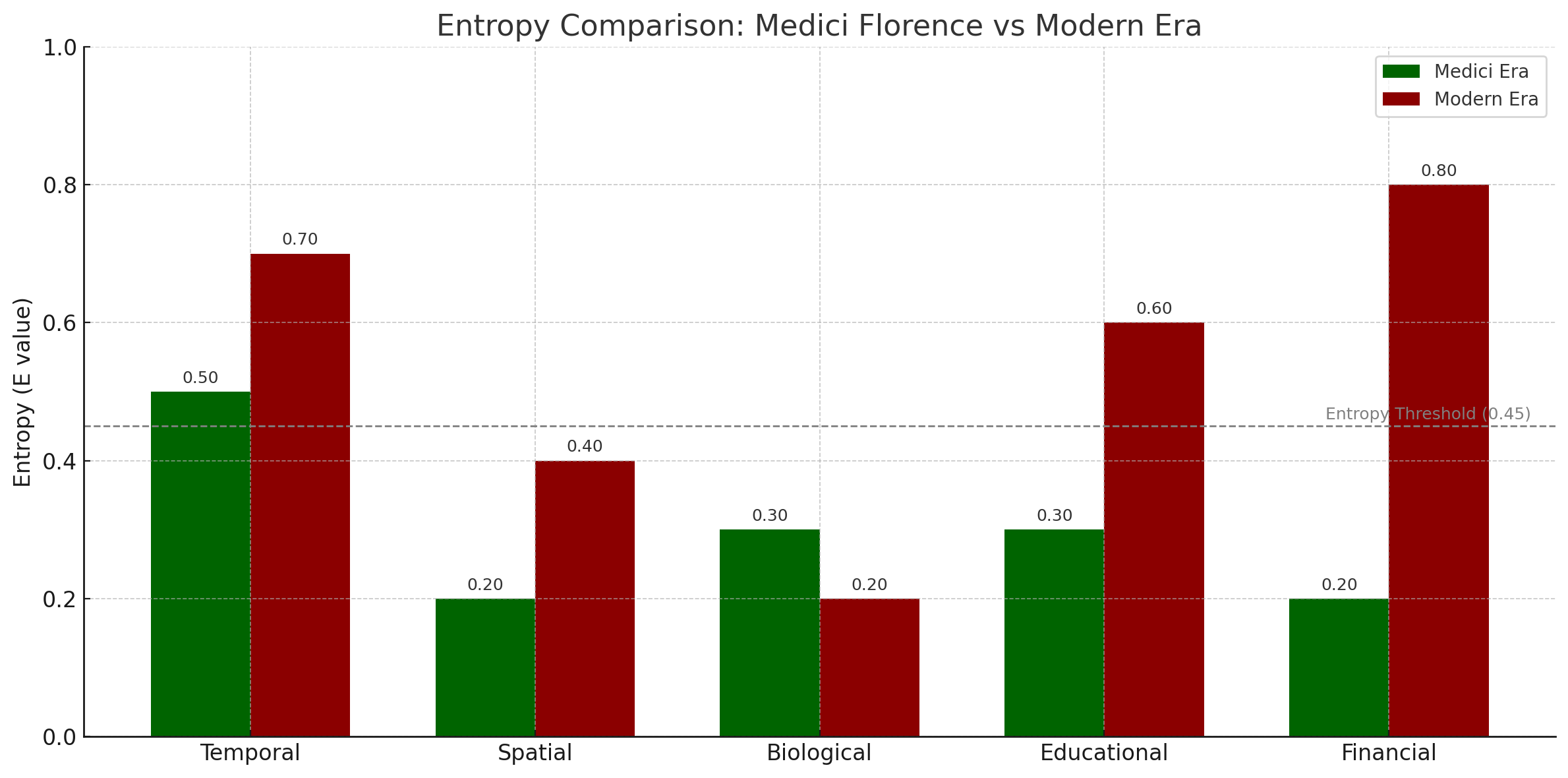
Despite massive advantages, Silicon Valley’s entropy levels prevent it from matching Renaissance Florence’s per capita innovation rate. Each dimension of entropy reveals specific failure modes that compound into systemic dysfunction.
Financial Entropy: The Valley’s Achilles Heel
The financial dimension reveals the starkest contrast between systems designed for human flourishing versus capital extraction. This single factor explains much of the innovation gap.
| Aspect | Renaissance Florence | Silicon Valley | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Funding Model | Patient patronage | VC expecting 10x returns | Support → Extraction |
| Income Security | Guaranteed stipends | Equity gambling | Stability → Volatility |
| Living Costs | Patron-provided | $3,500+/mo rent | Included → Crushing |
| Debt Burden | None | Student loans persist | Freedom → Constraint |
| Time Horizon | Decades | 18-month runways | Patient → Frantic |
- Florence: (Artists focused purely on craft)
- Silicon Valley: (Constant fundraising anxiety, burnout endemic)
The 0.4 entropy differential in the financial dimension alone explains much of the innovation gap between these systems.
Educational Entropy: Information Without Wisdom
Knowledge transfer systems determine how efficiently expertise propagates through populations. The contrast between Florence and Silicon Valley reveals dramatically different learning environments.
| Aspect | Renaissance Florence | Silicon Valley | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Model | Master-apprentice | Stack Overflow/YouTube | Mentorship → Self-serve |
| Knowledge Transfer | 7-year apprenticeships | 3-month bootcamps | Deep → Shallow |
| Signal/Noise Ratio | High (curated) | Low (information overload) | Clarity → Chaos |
| Skill Development | Complete mastery | Constant framework churn | Stable → Shifting |
| Access to Masters | Daily interaction | Rare unless hired | Included → Transactional |
- Florence: (Clear progression to mastery)
- Silicon Valley: (Endless learning without mastery)
The educational entropy gap means modern learners navigate chaos while Renaissance apprentices followed proven paths to mastery. This educational dysfunction compounds with physical arrangement challenges, creating cascading inefficiencies.
Spatial Entropy: Proximity Without Connection
Physical arrangement significantly impacts innovation emergence through encounter probability and collaboration ease. Geography shapes innovation outcomes more than most realize.
| Aspect | Renaissance Florence | Silicon Valley | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geographic Span | 15-min walk | 50-mile sprawl | Walkable → Commute |
| Collaboration Space | Shared workshops | Isolated offices | Open → Siloed |
| Serendipity | Constant street encounters | Scheduled meetings | Natural → Forced |
| Living Patterns | Artists lived at workshops | 2-hour commutes | Integrated → Separated |
| Community Formation | Organic neighborhoods | Transient population | Stable → Fluid |
- Florence: (Everything within walking distance)
- Silicon Valley: (Sprawl despite concentration)
Lower spatial energy multiplier in Florence created inevitable collaboration while Silicon Valley requires deliberate coordination, increasing thermodynamic costs for information exchange.
Temporal Entropy: The Speed Trap
Time structures determine sustainable innovation capacity over entire careers within the boundary information processing system.
| Aspect | Renaissance Florence | Silicon Valley | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work Rhythms | Natural light cycles | 24/7 always-on | Sustainable → Burnout |
| Project Timelines | Years for masterworks | Ship weekly | Deep → Surface |
| Career Stability | Lifetime patronage | 1.8 year average tenure | Committed → Transient |
| Focus Time | Uninterrupted days | Constant interruptions | Flow → Fragmentation |
| Success Metrics | Artistic achievement | Growth metrics | Quality → Quantity |
- Florence: (Natural rhythms respected)
- Silicon Valley: (Artificial urgency dominates)
Equal temporal entropy masks different failure modes—Florence accepted natural limits while Silicon Valley fights them, creating additional thermodynamic burdens.
Biological Entropy: Wealth Without Wellness
Basic human requirements create baseline entropy that compounds across all other dimensions within the cosmic information processing framework.
| Aspect | Renaissance Florence | Silicon Valley | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Needs | Patron-provided | Market-rate everything | Secured → Anxious |
| Healthcare | Patron’s physician | Insurance complexity | Simple → Bureaucratic |
| Nutrition | Fresh local food | Soylent and takeout | Natural → Optimized |
| Exercise | Walking city | Gym memberships | Integrated → Scheduled |
| Stress Levels | Moderate | Epidemic burnout | Manageable → Overwhelming |
- Florence: (Basic needs met simply)
- Silicon Valley: (Wealth without security)
The biological entropy difference compounds across every waking hour, draining energy from innovation within the discrete spacetime constraints. These entropy dimensions combine to create measurable thermodynamic burdens that can be quantified through mathematical analysis of system efficiency.
Mathematical Analysis of Innovation Efficiency
Mathematical analysis demonstrates how Silicon Valley falls short despite massive advantages when conscious agents operate within the boundary information processing framework established by the cosmic collision.
Innovation Density Analysis
The per capita analysis exposes the scale of underperformance within the electromagnetic voxel lattice constraints:
- Florence: 3.9 innovators per 10,000 people
- Silicon Valley: 0.32 innovators per 10,000 people
- Expected innovators (Florence rate): ~30,000
- Actual innovators: ~2,500
- Innovation deficit: 91.7%
Silicon Valley should produce 30,000 major innovators at Florence’s rate but manages less than a tenth of that potential when operating within identical cosmic information processing constraints.
The Efficiency Calculation
The equation reveals systemic efficiency differences within the unified Information Physics framework:
For JOIN operations with aligned intent : Silicon Valley achieves 16% less entropy reduction per effort when operating within the discrete spacetime substrate.
This efficiency gap compounds with thermodynamic costs from information processing within the electromagnetic voxel lattice. The analysis indicates innovators burn 9.2x more energy while achieving 16% less impact—a double penalty that explains the 12x per capita innovation decline.
Career Hierarchy as Thermodynamic Gradient
Mapping career roles to their thermodynamic burdens reveals how system design affects every level within the cosmic information processing framework:
| Level | Florence Role | Silicon Valley Role | (Florence) | (SV) | (Florence) | (SV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Apprentice | Junior Engineer | 0.50 | 0.75 | 1.333 | 1.143 |
| Mid | Journeyman | Senior Engineer | 0.35 | 0.55 | 1.481 | 1.290 |
| Expert | Master | Principal Engineer | 0.25 | 0.40 | 1.600 | 1.429 |
| Sponsor | Patron | CEO/VC | 0.15 | 0.20 | 1.739 | 1.667 |
Even entry-level positions show the pattern: Florence apprentices outperform Silicon Valley junior engineers despite technology gaps when operating within identical boundary information processing constraints. The thermodynamic advantage compounds up the hierarchy.
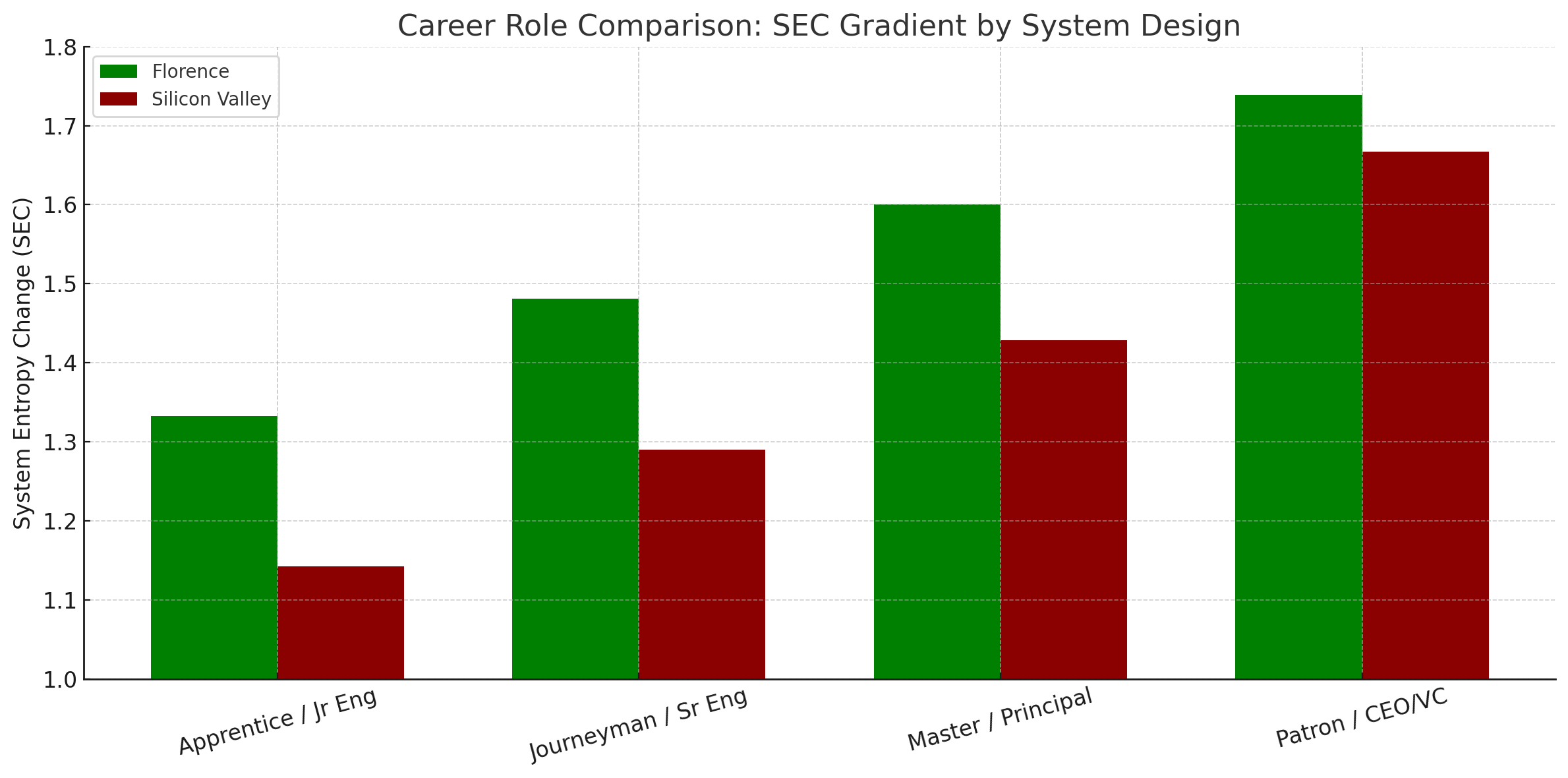
Why Silicon Valley ≠ Renaissance Florence
The thermodynamic analysis reveals that despite surface similarities, core differences in system design create vastly different entropy conditions within the electromagnetic voxel lattice constraints. These architectural choices explain the innovation gap when conscious agents navigate identical cosmic information processing requirements, demonstrating how structural decisions compound into measurable performance differences.
The Medici Model vs VC Model
The funding models create opposite entropy dynamics within the boundary information processing framework:
Medici Patronage:
- Patient capital seeking prestige
- Decades-long support
- Housing and needs included
- Success = artistic achievement
- Patron-artist alignment
Venture Capital:
- Impatient capital seeking returns
- 5-7 year fund cycles
- Everything market-rate
- Success = financial exit
- Investor-founder misalignment
The structural misalignment in Silicon Valley creates entropy that Florence avoided through aligned incentives when conscious agents operate within the cosmic collision-diffusion dynamics.
Physical Architecture Differences
The built environment encodes entropy into daily experience within the discrete spacetime substrate.
Florence:
- Walkable city center
- Mixed-use neighborhoods
- Artists lived above workshops
- Public squares for interaction
- Human-scale architecture
Silicon Valley:
- Car-dependent sprawl
- Zoned separation
- Commuter bedroom communities
- Private campuses
- Inhuman scale
Florence’s architecture facilitated low-entropy interaction while Silicon Valley’s enforces high-entropy separation, increasing thermodynamic costs for information exchange within the electromagnetic voxel lattice.
Cultural Operating System
The underlying cultural values shape entropy accumulation within the cosmic information processing framework.
Florence:
- Celebration of mastery
- Public art everywhere
- Competitive collaboration
- Long-term thinking
- Beauty as priority
Silicon Valley:
- Celebration of exits
- Private wealth hidden
- Zero-sum competition
- Quarterly thinking
- Efficiency as priority
These value differences create self-reinforcing entropy patterns in each system when conscious agents navigate the boundary information gradients established by the collision. The cumulative effect of these architectural, funding, and cultural differences pushes Silicon Valley beyond sustainable entropy levels, triggering cascade dynamics that mirror cosmic information processing breakdown.
The Approaching Cascade
At , Silicon Valley has exceeded the critical percolation threshold where cascading failures become self-reinforcing within the boundary information processing framework. Having crossed , the system now experiences accelerating dysfunction that follows predictable mathematical patterns.
Thermodynamic Parallels with Cosmic Information Processing
The innovation ecosystem analysis reveals striking parallels with the collision-diffusion mechanism that governs cosmic evolution. Just as the information-reaction term peaks at redshift and then decays, innovation systems exhibit similar patterns when entropy accumulation overwhelms structure-forming processes.
Recent thermodynamic calculations suggest concrete energy costs within the electromagnetic voxel lattice constraints:
- Florence innovator: kcal/day entropy burden
- Silicon Valley innovator: kcal/day entropy burden
- Energy multiplication: higher cost for same outcomes
- Information processing: bits/hour (SV) vs bits/hour (Florence)
- Movement entropy: 15km equivalent (SV) vs 3km walk (Florence)
These calculations map directly to survival curves within the cosmic information processing system. Assuming equal starting energy reserves of 100,000 kcal, Florence innovators sustain operations for 90+ days while Silicon Valley innovators exhaust reserves by day 55. The mathematics indicate thermodynamic exhaustion, not motivational failure, drives innovation collapse.
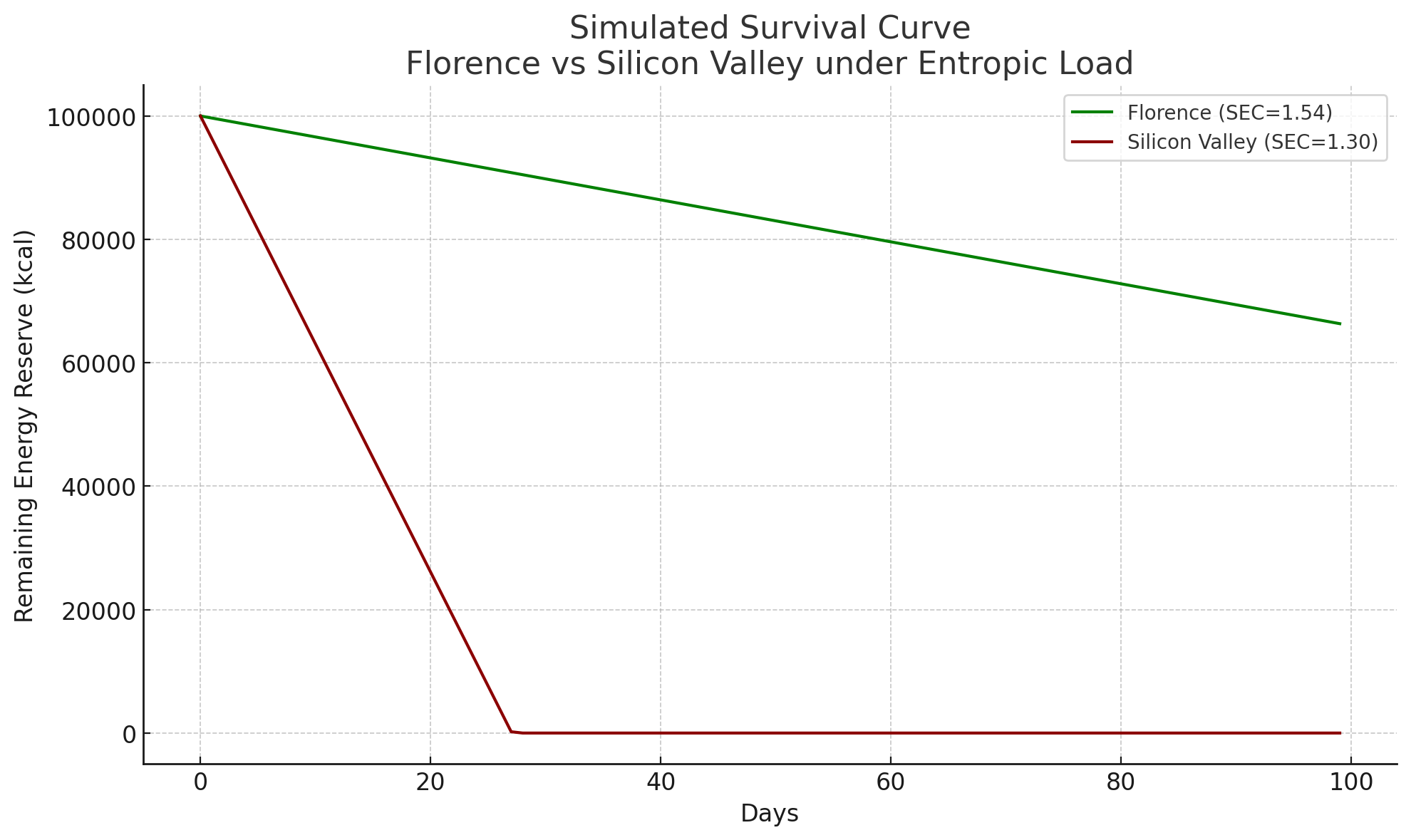
Warning Signs Within the Framework
Current symptoms indicate a system under critical stress within the boundary information processing constraints:
- Talent exodus: Engineers fleeing to Austin, Miami, remote
- Shortened horizons: Focus shifting from moonshots to quick exits
- Cultural decay: “Tech bro” culture replacing builder culture
- Innovation slowdown: More unicorns, fewer breakthroughs
- Inequality spiral: Success increasingly concentrated
Each symptom reflects mathematical proximity to cascade threshold where the collision-diffusion mechanism can no longer maintain stable information processing patterns.
Cascade Triggers
Several factors could push Silicon Valley past sustainable entropy levels within the cosmic information processing framework:
- Housing costs exceeding $4k/mo average: Spatial entropy spike
- AI replacing junior roles: Educational entropy increase
- Climate/fire disruptions: Biological entropy rise
- Remote work normalization: Spatial entropy expansion
- Economic downturn: Financial entropy explosion
Any of these could trigger the phase transition from functional to dysfunctional system within the electromagnetic voxel lattice constraints.
Breaking the Pattern
Silicon Valley could learn from Florence’s low-entropy design within the boundary information processing framework. The mathematics indicate specific interventions with measurable impact when conscious agents operate within cosmic collision-diffusion dynamics.
Immediate Interventions
Actions requiring no structural reform within the discrete spacetime substrate:
- Corporate housing programs: Reduce financial/spatial energy multiplier
- Apprenticeship programs: Replace bootcamps with real mentorship
- Mixed-use development: Enable walking communities
- Patient capital funds: 20-year horizons, not 5
- Public celebration spaces: Make innovation visible
Each intervention targets specific entropy dimensions with measurable reduction effects when operating within the electromagnetic voxel lattice constraints.
Structural Reforms
Systemic changes requiring coordinated action within the cosmic information processing framework:
- Universal basic income experiments: Reduce financial anxiety
- Zoning reform: Allow Florence-style mixed use
- Transportation redesign: Reduce commute entropy
- Education partnerships: Formal apprenticeships with tech masters
- Cultural renaissance: Prioritize beauty alongside utility
The mathematics indicate small improvements could have massive impact near the percolation threshold when conscious agents navigate the boundary information gradients established by the collision.
Comparing Innovation Hubs
Global innovation centers can be evaluated through the same entropy framework within the unified Information Physics system:
| Innovation Hub | Population | η Value | Status | Key Constraint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renaissance Florence | 70,000 | 0.30 | Optimal | Limited scale |
| Silicon Valley | 7.7M | 0.54 | Exceeded | Financial entropy |
| Shenzhen | 17.5M | 0.41 | Functional | Spatial entropy |
| London Tech City | 500k | 0.46 | Critical | Exceeded threshold |
| Bangalore | 13M | 0.38 | Promising | Rising fast |
Silicon Valley’s indicates it has crossed into thermodynamic dysfunction, operating far below Florence’s efficiency despite being the most resourced modern hub when measured within the boundary information processing framework.
Entropy-Induced Energy Costs by Source
Thermodynamic analysis reveals where entropy accumulates into measurable energy burdens within the electromagnetic voxel lattice constraints. Each source contributes to the total daily caloric cost innovators must pay simply to maintain position.
| Entropy Source | Florence (kcal/day) | Silicon Valley (kcal/day) | Multiplication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commute/Movement | 120 | 600 | 5.0x |
| Financial Stress | 0 | 400 | ∞ |
| Temporal Entropy | 160 | 160 | 1.0x |
| Nutritional Inefficiency | 0 | 100 | ∞ |
| Collaboration Overhead | 50 | 300 | 6.0x |
| Total | 170 | 1,560 | 9.2x |
The analysis indicates Silicon Valley innovators expend nearly ten times more energy on entropy management within the cosmic information processing system, leaving proportionally less for actual innovation. This thermodynamic burden explains why a city with every advantage produces fewer breakthroughs per capita than Renaissance Florence when operating within identical boundary information processing constraints.
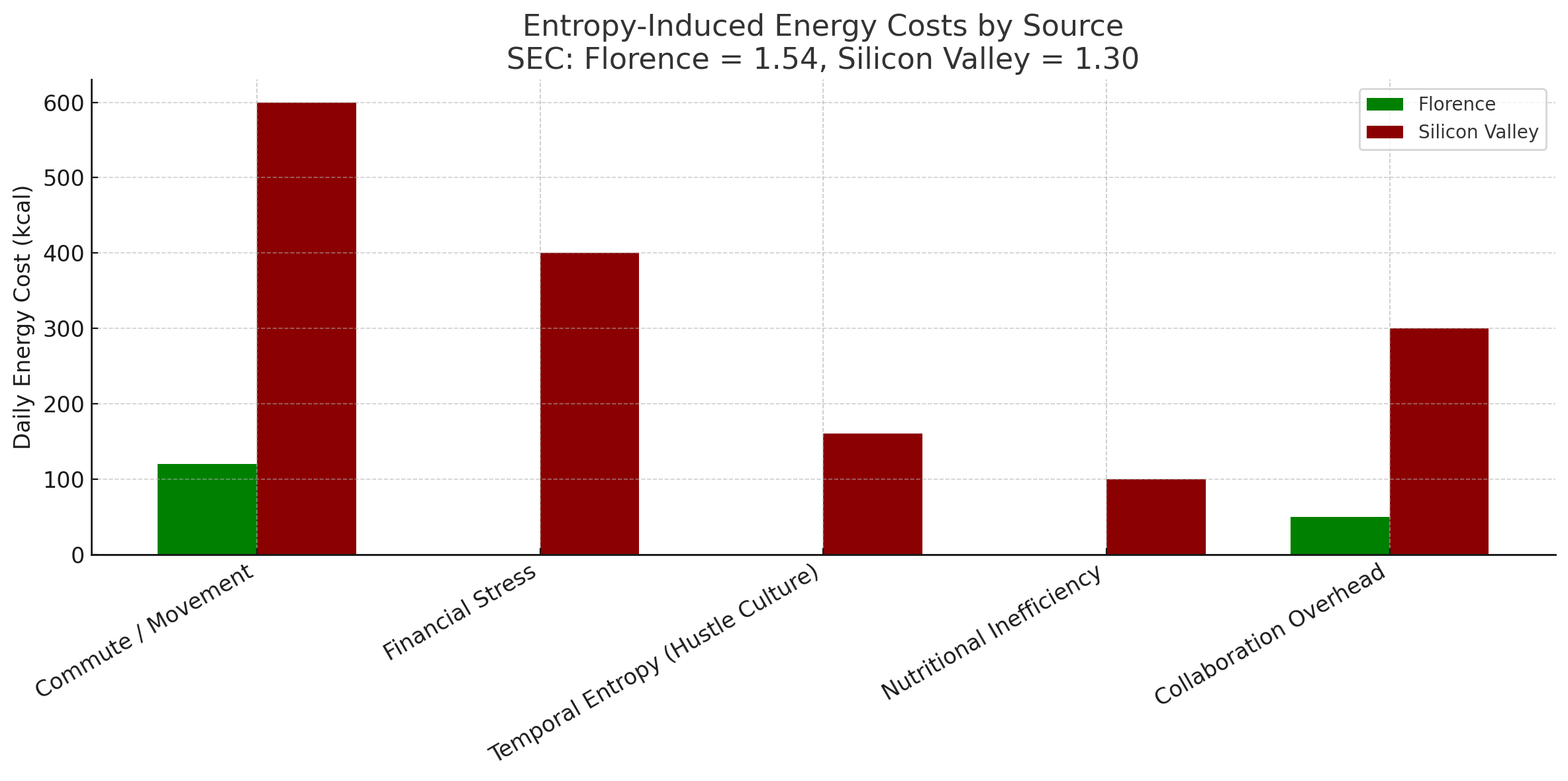
Validation Requirements
Disclaimer: This theoretical framework requires extensive empirical validation before acceptance as established theory within the Information Physics system. The comparative analysis and mathematical calculations outlined above need systematic testing through:
- Longitudinal studies measuring actual innovation rates and energy expenditure across different innovation ecosystems
- Metabolic and cognitive load studies validating thermodynamic calculations for innovators in different environments
- Statistical analysis of career trajectory data comparing Florence-era and Silicon Valley innovation patterns
- Cross-cultural validation of entropy measurements across diverse innovation hubs globally
- Economic analysis confirming the relationship between funding models and innovation outcomes
- Spatial analysis studies measuring the impact of urban design on collaboration and innovation rates
- Historical verification of Renaissance Florence innovation metrics and comparison methodologies
- Peer review and independent verification across economics, urban planning, and innovation studies disciplines
While The Innovation Entropy Crisis offers compelling mathematical consistency and observable pattern correlations within the unified Information Physics framework, it represents a speculative theoretical framework that must undergo rigorous empirical validation through comparative studies, experimental confirmation, and interdisciplinary scrutiny before acceptance as established innovation science.
Conclusion: The Mathematical Warning
Silicon Valley and Renaissance Florence face identical fundamental conditions—all innovation systems are entropically constrained and systemically bounded. The difference lies in navigation capability.
Florence provided time (patient patronage) and information clarity (master-apprentice relationships) as effective navigation tools. Silicon Valley compresses time while drowning information in noise, leaving innovators unable to navigate despite superior resources.
The mathematics are clear: Silicon Valley operates at compared to Florence’s , achieving 16% less while burning 9.2× more energy. This represents navigation failure—when consciousness cannot effectively use time and information to work around constraints, even the most resourced systems fail.
Until Silicon Valley reduces entropy below across all dimensions—particularly the crushing financial entropy of —it will continue wasting human potential.
The Medici model versus the VC model: The Medici created optimal conditions for human flourishing through deliberate entropy reduction. Silicon Valley creates wealth while maintaining entropy levels that make true innovation exponentially harder than necessary.
The mathematics indicate that only systematic entropy reduction can unlock Silicon Valley’s true potential. Positional energy multiplier compounds with systemic entropy, creating measurable energy burdens that affect the ability to contribute, create, and survive.
This pattern offers a parsimonious explanation grounded in measurable energy, position, and mathematical causality rather than abstract psychological theories. The thermodynamic reality is clear: innovation systems must operate below critical entropy thresholds to sustain breakthrough creation.
Cross-References
The following components complete the Information Physics framework:
- Collision Theory (CDE): Cosmic origins and boundary information dynamics through collision-diffusion mechanisms
- Electromagnetic Voxel Lattice Theory (EVL): Discrete spacetime substrate and information processing constraints within the voxel lattice
- Information Physics Theory (IP): Consciousness and memory within cosmic information processing systems
- Entropic Mechanics (EM): Observer-dependent navigation of information gradients and entropy management
- Notation and Symbols Table: Complete mathematical framework and cross-framework consistency
These components work together to provide a comprehensive understanding of reality from cosmic collision to innovation system dynamics through unified information processing principles.